Introduction:
The refraction of light through a prism is a captivating phenomenon that has intrigued scientists and curious minds for centuries. In this article, we will explore the concept of refraction, delve into the workings of a prism, and understand how light undergoes this intriguing process. Join us on a journey through the prism to unravel the secrets of refraction and its mesmerizing effects.
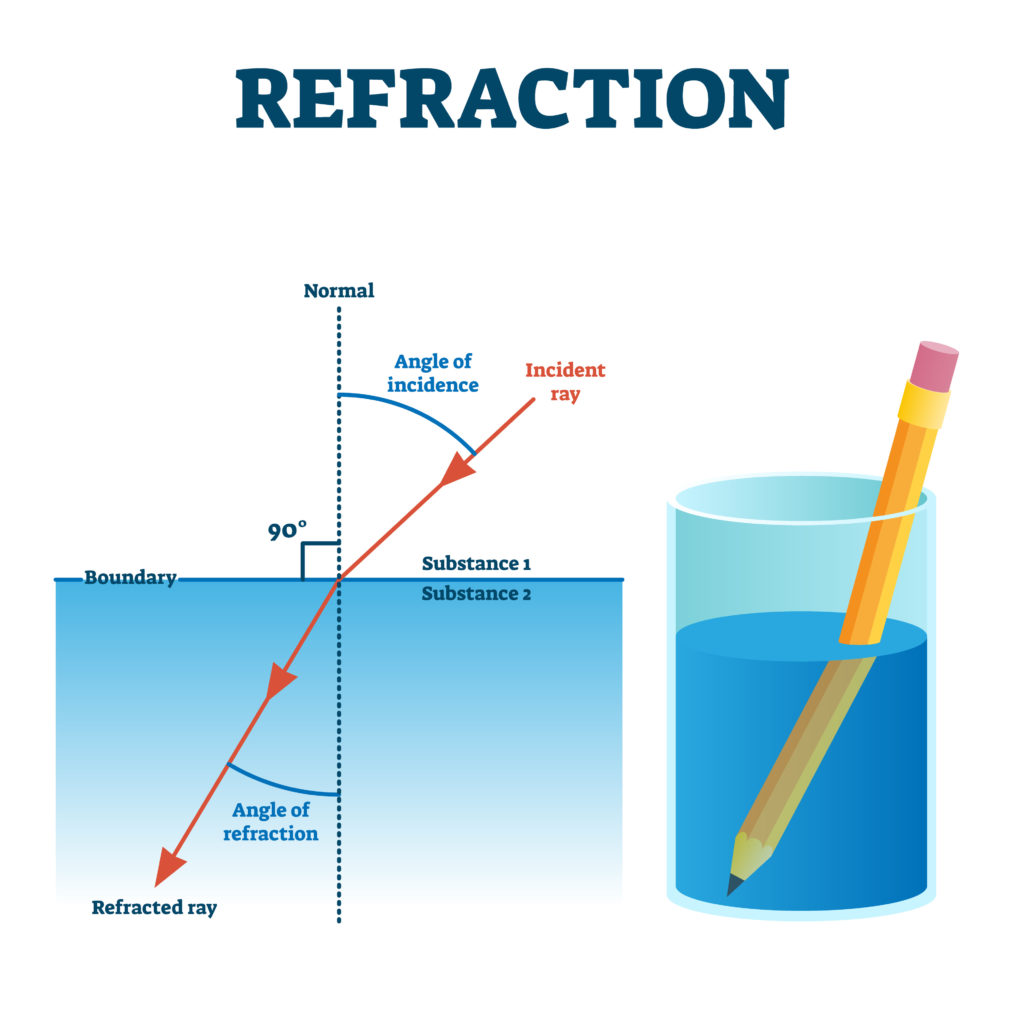
What is Refraction and How Does it Work?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through different mediums, such as air, water, or glass. It occurs due to a change in the speed of light when it transitions from one medium to another. The bending of light is a result of its interaction with the atoms and molecules in the new medium, causing a change in its direction.
The Prism: A Key Player in Refraction
A prism is a transparent optical element with two triangular ends and rectangular faces. It is typically made of glass or plastic and is renowned for its ability to disperse white light into a spectrum of colors. When light enters a prism, it undergoes refraction, causing the light rays to bend and separate into its constituent colors.
The Role of Angle and Shape in Prism Refraction
The angle at which light enters the prism, known as the angle of incidence, determines the extent to which the light bends upon refraction. This angle, in combination with the shape and refractive properties of the prism, influences the dispersion of light and the formation of a rainbow-like spectrum.
Dissecting the Rainbow: Dispersion of Light by a Prism
White light is composed of a combination of colors with different wavelengths. As light enters a prism, it encounters a change in speed and refractive index. This causes each color component of white light to refract at slightly different angles, resulting in the separation of colors and the formation of a spectrum.
Exploring the Prism’s Refractive Index and Material Properties
The refractive index of a prism, determined by the material it is made of, plays a crucial role in the amount of bending and dispersion that occurs. Different materials have varying refractive indexes, leading to different degrees of refraction and dispersion. This property allows scientists to manipulate and control the effects of refraction.
Applications of Prism Refraction in Science and Technology
The refraction of light through a prism finds numerous practical applications in various fields. Prisms are integral components in optical instruments like cameras, telescopes, and microscopes, allowing for precise focusing and image formation. They are also used in spectroscopy to analyze the composition of substances based on their light absorption and emission patterns.
The Beauty and Wonder of Prism Refraction
Beyond its scientific applications, the refraction of light through a prism captivates our senses and sparks our imagination. The enchanting sight of a rainbow, created by sunlight refracting through raindrops, is a vivid example of the mesmerizing effects of prism refraction in nature.
Conclusion:
The refraction of light through a prism unveils a fascinating world of optical wonders. By bending and dispersing light, prisms reveal the hidden spectrum of colors that comprise white light. Understanding the principles behind prism refraction helps us appreciate the intricate workings of light and its interaction with various mediums. From scientific applications to the sheer beauty of rainbows, prism refraction continues to captivate and inspire us, shedding light on the remarkable phenomenon that shapes our visual experiences.